Mazgaon, Mumbai, Maharashtra
- GST NO. : 27ABCFP8811D1ZC
1.00 / piece
| Business Type | Manufacturer, Supplier, Retailer |
| Application | Electric Equipment |
| Feature | Corrosion Resistant, Fine Finish, Highly Durable |
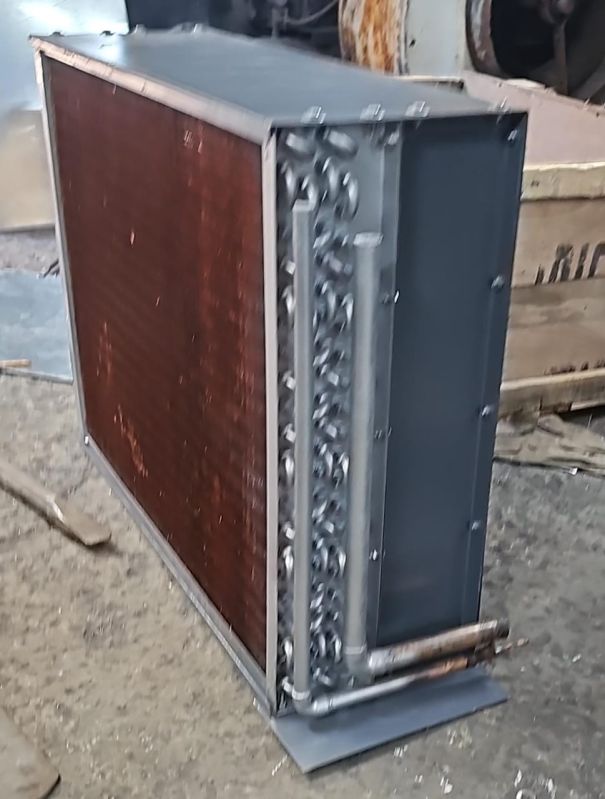
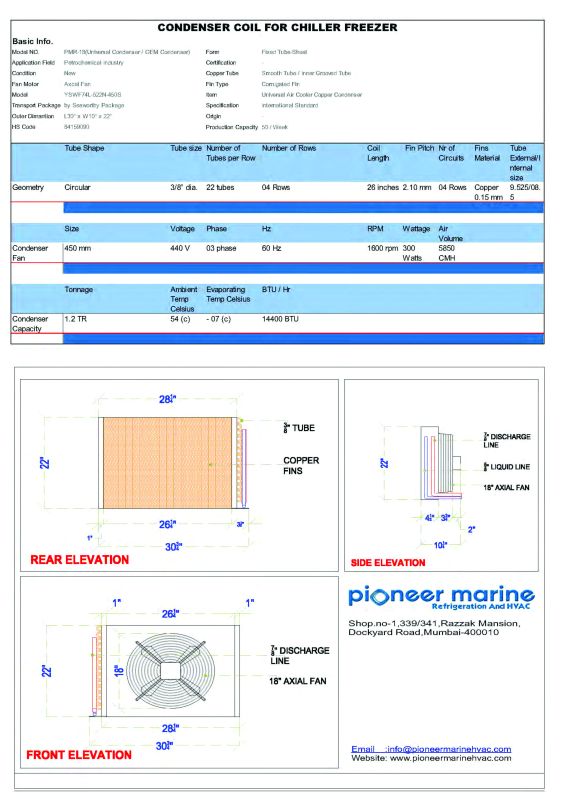
| Type | Condensing Coils |
| Click to view more | |
Product Details
Country of Origin
India
Product Code
PMR-Condenser Coil
Port
mumbai
These vital components play a crucial role in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Here’s a concise breakdown of what you need to know:
- Types of Condensing Units:
- Air-Cooled Condensing Units: These units dissipate heat by using ambient air. They’re commonly seen on rooftops or alongside buildings. The cooling process involves a fan blowing air over the condenser coils, releasing heat into the atmosphere.
- Water-Cooled Condensing Units: Instead of relying on air, these units use water as the cooling medium. They’re often found in industrial settings where air-cooling might be less efficient due to high ambient temperatures.
- Hermetic and Semi-Hermetic Styles:
- Hermetic: In hermetic condensing units, the compressor and motor are sealed within a single housing. This design ensures that the refrigerant remains isolated from the external environment. Hermetic units are commonly used in smaller applications like residential air conditioners and refrigerators.
- Semi-Hermetic: Semi-hermetic units have a serviceable compressor. The housing can be opened for maintenance or repairs. These units are more robust and are often employed in commercial and industrial systems.
- Compressor Configurations:
- Piston Parallel: This configuration features reciprocating (piston) compressors arranged in parallel. It’s efficient and reliable for various cooling needs.
- Screw: Screw compressors are commonly used in larger systems. They provide continuous compression and are well-suited for industrial-scale applications.
Remember, the efficiency of a condensing unit impacts the overall performance of your cooling system. Whether it’s keeping your ice cream frozen or maintaining a comfortable office temperature, these units quietly work behind the scenes to keep things just right.
Looking for "CONDENSER COIL FOR CHILLER FREEZER" ?
p
Explore More Products